Chapter 19: Life in the Universe
Chapter 1
How Science Works
- The Scientific Method
- Evidence
- Measurements
- Units and the Metric System
- Measurement Errors
- Estimation
- Dimensions
- Mass, Length, and Time
- Observations and Uncertainty
- Precision and Significant Figures
- Errors and Statistics
- Scientific Notation
- Ways of Representing Data
- Logic
- Mathematics
- Geometry
- Algebra
- Logarithms
- Testing a Hypothesis
- Case Study of Life on Mars
- Theories
- Systems of Knowledge
- The Culture of Science
- Computer Simulations
- Modern Scientific Research
- The Scope of Astronomy
- Astronomy as a Science
- A Scale Model of Space
- A Scale Model of Time
- Questions
Chapter 2
Early Astronomy
- The Night Sky
- Motions in the Sky
- Navigation
- Constellations and Seasons
- Cause of the Seasons
- The Magnitude System
- Angular Size and Linear Size
- Phases of the Moon
- Eclipses
- Auroras
- Dividing Time
- Solar and Lunar Calendars
- History of Astronomy
- Stonehenge
- Ancient Observatories
- Counting and Measurement
- Astrology
- Greek Astronomy
- Aristotle and Geocentric Cosmology
- Aristarchus and Heliocentric Cosmology
- The Dark Ages
- Arab Astronomy
- Indian Astronomy
- Chinese Astronomy
- Mayan Astronomy
- Questions
Chapter 3
The Copernican Revolution
- Ptolemy and the Geocentric Model
- The Renaissance
- Copernicus and the Heliocentric Model
- Tycho Brahe
- Johannes Kepler
- Elliptical Orbits
- Kepler's Laws
- Galileo Galilei
- The Trial of Galileo
- Isaac Newton
- Newton's Law of Gravity
- The Plurality of Worlds
- The Birth of Modern Science
- Layout of the Solar System
- Scale of the Solar System
- The Idea of Space Exploration
- Orbits
- History of Space Exploration
- Moon Landings
- International Space Station
- Manned versus Robotic Missions
- Commercial Space Flight
- Future of Space Exploration
- Living in Space
- Moon, Mars, and Beyond
- Societies in Space
- Questions
Chapter 4
Matter and Energy in the Universe
- Matter and Energy
- Rutherford and Atomic Structure
- Early Greek Physics
- Dalton and Atoms
- The Periodic Table
- Structure of the Atom
- Energy
- Heat and Temperature
- Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Velocity of Gas Particles
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Heat Transfer
- Thermal Radiation
- Wien's Law
- Radiation from Planets and Stars
- Internal Heat in Planets and Stars
- Periodic Processes
- Random Processes
- Questions
Chapter 5
The Earth-Moon System
- Earth and Moon
- Early Estimates of Earth's Age
- How the Earth Cooled
- Ages Using Radioactivity
- Radioactive Half-Life
- Ages of the Earth and Moon
- Geological Activity
- Internal Structure of the Earth and Moon
- Basic Rock Types
- Layers of the Earth and Moon
- Origin of Water on Earth
- The Evolving Earth
- Plate Tectonics
- Volcanoes
- Geological Processes
- Impact Craters
- The Geological Timescale
- Mass Extinctions
- Evolution and the Cosmic Environment
- Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans
- Weather Circulation
- Environmental Change on Earth
- The Earth-Moon System
- Geological History of the Moon
- Tidal Forces
- Effects of Tidal Forces
- Historical Studies of the Moon
- Lunar Surface
- Ice on the Moon
- Origin of the Moon
- Humans on the Moon
- Questions
Chapter 6
The Terrestrial Planets
- Studying Other Planets
- The Planets
- The Terrestrial Planets
- Mercury
- Mercury's Orbit
- Mercury's Surface
- Venus
- Volcanism on Venus
- Venus and the Greenhouse Effect
- Tectonics on Venus
- Exploring Venus
- Mars in Myth and Legend
- Early Studies of Mars
- Mars Close-Up
- Modern Views of Mars
- Missions to Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Water on Mars
- Polar Caps of Mars
- Climate Change on Mars
- Terraforming Mars
- Life on Mars
- The Moons of Mars
- Martian Meteorites
- Comparative Planetology
- Incidence of Craters
- Counting Craters
- Counting Statistics
- Internal Heat and Geological Activity
- Magnetic Fields of the Terrestrial Planets
- Mountains and Rifts
- Radar Studies of Planetary Surfaces
- Laser Ranging and Altimetry
- Gravity and Atmospheres
- Normal Atmospheric Composition
- The Significance of Oxygen
- Questions
Chapter 7
The Giant Planets and Their Moons
- The Gas Giant Planets
- Atmospheres of the Gas Giant Planets
- Clouds and Weather on Gas Giant Planets
- Internal Structure of the Gas Giant Planets
- Thermal Radiation from Gas Giant Planets
- Life on Gas Giant Planets?
- Why Giant Planets are Giant
- Gas Laws
- Ring Systems of the Giant Planets
- Structure Within Ring Systems
- The Origin of Ring Particles
- The Roche Limit
- Resonance and Harmonics
- Tidal Forces in the Solar System
- Moons of Gas Giant Planets
- Geology of Large Moons
- The Voyager Missions
- Jupiter
- Jupiter's Galilean Moons
- Jupiter's Ganymede
- Jupiter's Europa
- Jupiter's Callisto
- Jupiter's Io
- Volcanoes on Io
- Saturn
- Cassini Mission to Saturn
- Saturn's Titan
- Saturn's Enceladus
- Discovery of Uranus and Neptune
- Uranus
- Uranus' Miranda
- Neptune
- Neptune's Triton
- Pluto
- The Discovery of Pluto
- Pluto as a Dwarf Planet
- Dwarf Planets
- Questions
Chapter 8
Interplanetary Bodies
- Interplanetary Bodies
- Comets
- Early Observations of Comets
- Structure of the Comet Nucleus
- Comet Chemistry
- Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt
- Kuiper Belt
- Comet Orbits
- Life Story of Comets
- The Largest Kuiper Belt Objects
- Meteors and Meteor Showers
- Gravitational Perturbations
- Asteroids
- Surveys for Earth Crossing Asteroids
- Asteroid Shapes
- Composition of Asteroids
- Introduction to Meteorites
- Origin of Meteorites
- Types of Meteorites
- The Tunguska Event
- The Threat from Space
- Probability and Impacts
- Impact on Jupiter
- Interplanetary Opportunity
- Questions
Chapter 9
Planet Formation and Exoplanets
- Formation of the Solar System
- Early History of the Solar System
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum in a Collapsing Cloud
- Helmholtz Contraction
- Safronov and Planet Formation
- Collapse of the Solar Nebula
- Why the Solar System Collapsed
- From Planetesimals to Planets
- Accretion and Solar System Bodies
- Differentiation
- Planetary Magnetic Fields
- The Origin of Satellites
- Solar System Debris and Formation
- Gradual Evolution and a Few Catastrophies
- Chaos and Determinism
- Extrasolar Planets
- Discoveries of Exoplanets
- Doppler Detection of Exoplanets
- Transit Detection of Exoplanets
- The Kepler Mission
- Direct Detection of Exoplanets
- Properties of Exoplanets
- Implications of Exoplanet Surveys
- Future Detection of Exoplanets
- Questions
Chapter 10
Detecting Radiation from Space
- Observing the Universe
- Radiation and the Universe
- The Nature of Light
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Properties of Waves
- Waves and Particles
- How Radiation Travels
- Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
- The Doppler Effect
- Invisible Radiation
- Thermal Spectra
- The Quantum Theory
- The Uncertainty Principle
- Spectral Lines
- Emission Lines and Bands
- Absorption and Emission Spectra
- Kirchoff's Laws
- Astronomical Detection of Radiation
- The Telescope
- Optical Telescopes
- Optical Detectors
- Adaptive Optics
- Image Processing
- Digital Information
- Radio Telescopes
- Telescopes in Space
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Interferometry
- Collecting Area and Resolution
- Frontier Observatories
- Questions
Chapter 11
Our Sun: The Nearest Star
- The Sun
- The Nearest Star
- Properties of the Sun
- Kelvin and the Sun's Age
- The Sun's Composition
- Energy From Atomic Nuclei
- Mass-Energy Conversion
- Examples of Mass-Energy Conversion
- Energy From Nuclear Fission
- Energy From Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Reactions in the Sun
- The Sun's Interior
- Energy Flow in the Sun
- Collisions and Opacity
- Solar Neutrinos
- Solar Oscillations
- The Sun's Atmosphere
- Solar Chromosphere and Corona
- Sunspots
- The Solar Cycle
- The Solar Wind
- Effects of the Sun on the Earth
- Cosmic Energy Sources
- Questions
Chapter 12
Properties of Stars
- Stars
- Star Names
- Star Properties
- The Distance to Stars
- Apparent Brightness
- Absolute Brightness
- Measuring Star Distances
- Stellar Parallax
- Spectra of Stars
- Spectral Classification
- Temperature and Spectral Class
- Stellar Composition
- Stellar Motion
- Stellar Luminosity
- The Size of Stars
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law
- Stellar Mass
- Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Stellar Classification
- The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- Volume and Brightness Selected Samples
- Stars of Different Sizes
- Understanding the Main Sequence
- Stellar Structure
- Stellar Evolution
- Questions
Chapter 13
Star Birth and Death
- Star Birth and Death
- Understanding Star Birth and Death
- Cosmic Abundance of Elements
- Star Formation
- Molecular Clouds
- Young Stars
- T Tauri Stars
- Mass Limits for Stars
- Brown Dwarfs
- Young Star Clusters
- Cauldron of the Elements
- Main Sequence Stars
- Nuclear Reactions in Main Sequence Stars
- Main Sequence Lifetimes
- Evolved Stars
- Cycles of Star Life and Death
- The Creation of Heavy Elements
- Red Giants
- Horizontal Branch and Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
- Variable Stars
- Magnetic Stars
- Stellar Mass Loss
- White Dwarfs
- Supernovae
- Seeing the Death of a Star
- Supernova 1987A
- Neutron Stars and Pulsars
- Special Theory of Relativity
- General Theory of Relativity
- Black Holes
- Properties of Black Holes
- Questions
Chapter 14
The Milky Way
- The Distribution of Stars in Space
- Stellar Companions
- Binary Star Systems
- Binary and Multiple Stars
- Mass Transfer in Binaries
- Binaries and Stellar Mass
- Nova and Supernova
- Exotic Binary Systems
- Gamma Ray Bursts
- How Multiple Stars Form
- Environments of Stars
- The Interstellar Medium
- Effects of Interstellar Material on Starlight
- Structure of the Interstellar Medium
- Dust Extinction and Reddening
- Groups of Stars
- Open Star Clusters
- Globular Star Clusters
- Distances to Groups of Stars
- Ages of Groups of Stars
- Layout of the Milky Way
- William Herschel
- Isotropy and Anisotropy
- Mapping the Milky Way
- Questions
Chapter 15
Galaxies
- The Milky Way Galaxy
- Mapping the Galaxy Disk
- Spiral Structure in Galaxies
- Mass of the Milky Way
- Dark Matter in the Milky Way
- Galaxy Mass
- The Galactic Center
- Black Hole in the Galactic Center
- Stellar Populations
- Formation of the Milky Way
- Galaxies
- The Shapley-Curtis Debate
- Edwin Hubble
- Distances to Galaxies
- Classifying Galaxies
- Spiral Galaxies
- Elliptical Galaxies
- Lenticular Galaxies
- Dwarf and Irregular Galaxies
- Overview of Galaxy Structures
- The Local Group
- Light Travel Time
- Galaxy Size and Luminosity
- Mass to Light Ratios
- Dark Matter in Galaxies
- Gravity of Many Bodies
- Galaxy Evolution
- Galaxy Interactions
- Galaxy Formation
- Questions
Chapter 16
The Expanding Universe
- Galaxy Redshifts
- The Expanding Universe
- Cosmological Redshifts
- The Hubble Relation
- Relating Redshift and Distance
- Galaxy Distance Indicators
- Size and Age of the Universe
- The Hubble Constant
- Large Scale Structure
- Galaxy Clustering
- Clusters of Galaxies
- Overview of Large Scale Structure
- Dark Matter on the Largest Scales
- The Most Distant Galaxies
- Black Holes in Nearby Galaxies
- Active Galaxies
- Radio Galaxies
- The Discovery of Quasars
- Quasars
- Types of Gravitational Lensing
- Properties of Quasars
- The Quasar Power Source
- Quasars as Probes of the Universe
- Star Formation History of the Universe
- Expansion History of the Universe
- Questions
Chapter 17
Cosmology
- Cosmology
- Early Cosmologies
- Relativity and Cosmology
- The Big Bang Model
- The Cosmological Principle
- Universal Expansion
- Cosmic Nucleosynthesis
- Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- Discovery of the Microwave Background Radiation
- Measuring Space Curvature
- Cosmic Evolution
- Evolution of Structure
- Mean Cosmic Density
- Critical Density
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Age of the Universe
- Precision Cosmology
- The Future of the Contents of the Universe
- Fate of the Universe
- Alternatives to the Big Bang Model
- Space-Time
- Particles and Radiation
- The Very Early Universe
- Mass and Energy in the Early Universe
- Matter and Antimatter
- The Forces of Nature
- Fine-Tuning in Cosmology
- The Anthropic Principle in Cosmology
- String Theory and Cosmology
- The Multiverse
- The Limits of Knowledge
- Questions
Chapter 18
Life On Earth
- Nature of Life
- Chemistry of Life
- Molecules of Life
- The Origin of Life on Earth
- Origin of Complex Molecules
- Miller-Urey Experiment
- Pre-RNA World
- RNA World
- From Molecules to Cells
- Metabolism
- Anaerobes
- Extremophiles
- Thermophiles
- Psychrophiles
- Xerophiles
- Halophiles
- Barophiles
- Acidophiles
- Alkaliphiles
- Radiation Resistant Biology
- Importance of Water for Life
- Hydrothermal Systems
- Silicon Versus Carbon
- DNA and Heredity
- Life as Digital Information
- Synthetic Biology
- Life in a Computer
- Natural Selection
- Tree Of Life
- Evolution and Intelligence
- Culture and Technology
- The Gaia Hypothesis
- Life and the Cosmic Environment
The History of SETI
Speculation about life in the universe has a long and interesting history. Two thousand years ago, Plutarch wrote about "collections of matter, some of which are other worlds with their own skies and races of men and beasts." The Church declared the doctrine of the "plurality of worlds" to be heretical in the 11th century, and Giordano Bruno was burned at the stake in 1609 for proposing an infinity of worlds with life on them, although in fact some of his other heresies regarding the Bible bothered the Church more than his views of life beyond Earth.
Practical SETI began in 1820 when Carl Gauss suggested planting large tracts of Siberian forest in a graphical demonstration of the Pythagorean theorem. Joseph von Littrow in 1840 wanted to ignite kerosene-filled trenches in the Sahara Desert in an assortment of geometric shapes. Neither of these proposals was ever funded. At the turn of the century, the eccentric genius Nikola Tesla built enormous 150-foot electrical coils and strained the power production capacity of Colorado Springs in order to send radio signals to extraterrestrials. Tesla thought that he had detected signals from an extraterrestrial civilization, but in fact, he discovered the atmospheric phenomenon known as whistlers. Guglielmo Marconi also used his early radio technology to listen for signals from beyond Earth.
Modern SETI began with Project OZMA, which ran from 1959 to 1960. In this experiment, Frank Drake scanned across a 400-kHz band of radiation from the two nearest solar-type stars. Nothing conclusive was found. Since then, dozens of radio SETI projects have been conducted without any convincing sign of extraterrestrial intelligence. Of course, all of these experiments combined have searched only a tiny fraction of the cosmic "haystack," which is the vast number of targets and frequencies that must be scanned.
On October 12, 1992 — 500 years after Columbus' discovery of the New World — NASA began the most ambitious SETI project ever. The prosaically named Microwave Observing Project (MOP) searched more of the cosmic haystack in its first five minutes than all previous SETI experiments combined! The long time scales for sending and receiving messages led NASA to a passive strategy: to search for signals that may have been deliberately or accidentally sent our way long ago. The search strategy has two components. The first part consists of the detailed monitoring of the 1000 solar-type stars nearest the Sun. The second part involves a scan of the entire sky, to allow for the possibility of rarer but more powerful signals from across the Galaxy.
After funding was repeatedly cut by the U.S. Congress, SETI activists started to look for private sources of funding. The current plan, called Project Phoenix, is not funded by taxpayers at all. Famous corporate leaders and media moguls like Steve Jobs and Paul Allen and Steven Spielberg have provided millions of dollars for a new generation of SETI experiments. Even though Congress has been dubious, the public is entranced by the idea of making contact with intelligence far beyond the solar system. The SETI Institute, a non-profit research lab, has parceled out data from the current radio experiments to millions of people around the country. Each person runs a program that uses spare capacity on their PC to look for artificial signals in a stream of radio noise. In this way, SETI researchers can harness the power of millions of PCs to look for elusive evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence.
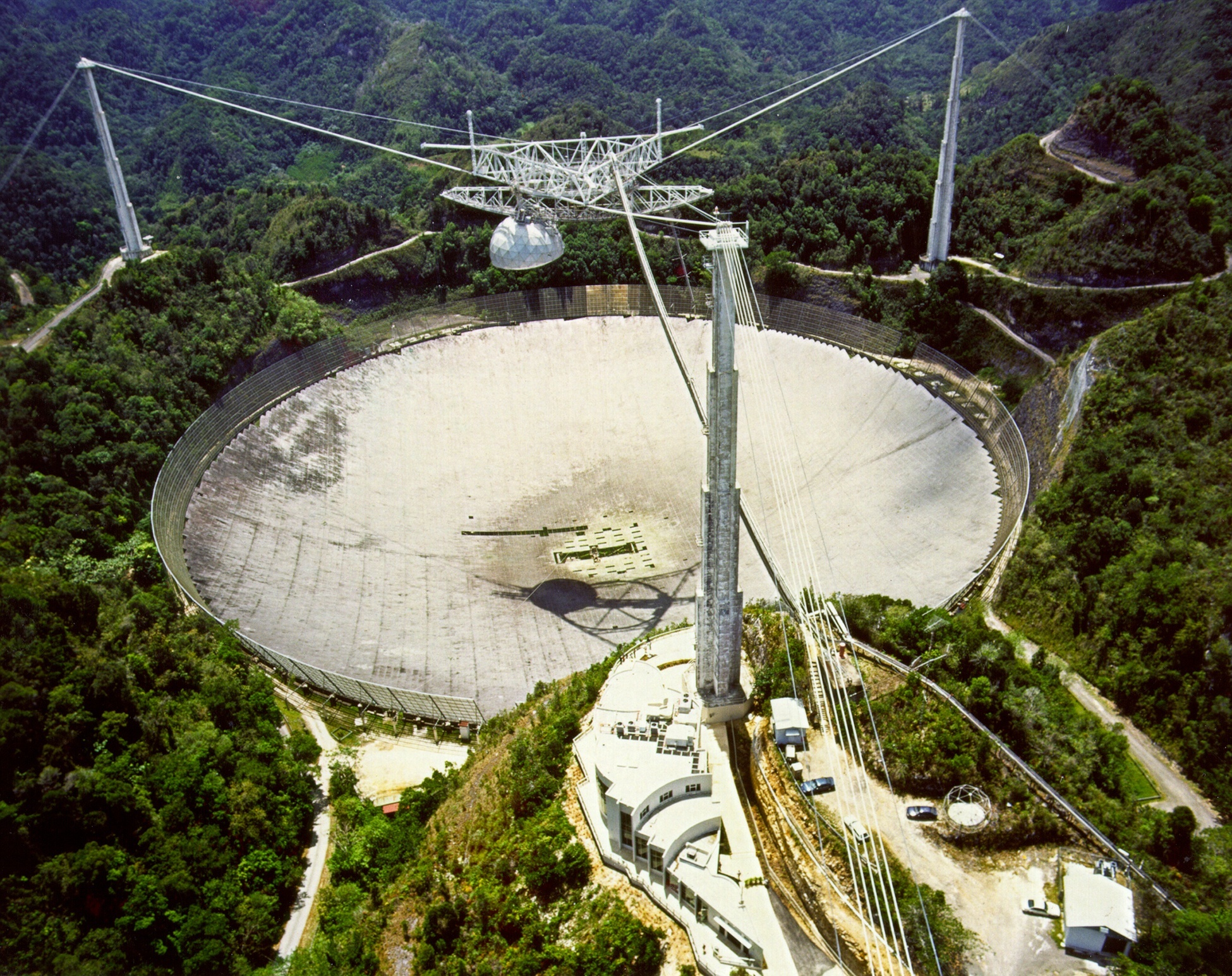

The new wave of SETI experiments depends on powerful receivers and large telescopes. Previous projects could only search a few hundred different frequency channels simultaneously. The MOP listened in on tens of millions of channels simultaneously. The improvement has been made possible by modern digital techniques and custom integrated circuits. The receivers are also extraordinarily sensitive. Astronomers achieved a radio detection of the weak signal of Pioneer 10 after it left the Solar System; the detection had a changing Doppler shift due to the Earth's rotation. The signal has the equivalent power of a single Christmas tree light at a distance of over 5 billion miles! The 1000-foot diameter radio dish at Arecibo in Puerto Rico offers even greater sensitivity. The dish is so large that it could hold 357 million boxes of corn flakes or all the beer consumed on Earth in one year. Detectors at the focus of the Arecibo dish could detect a ½ megawatt radio signal, equal to the strength of a modest radio station, on the other side of the Milky Way.
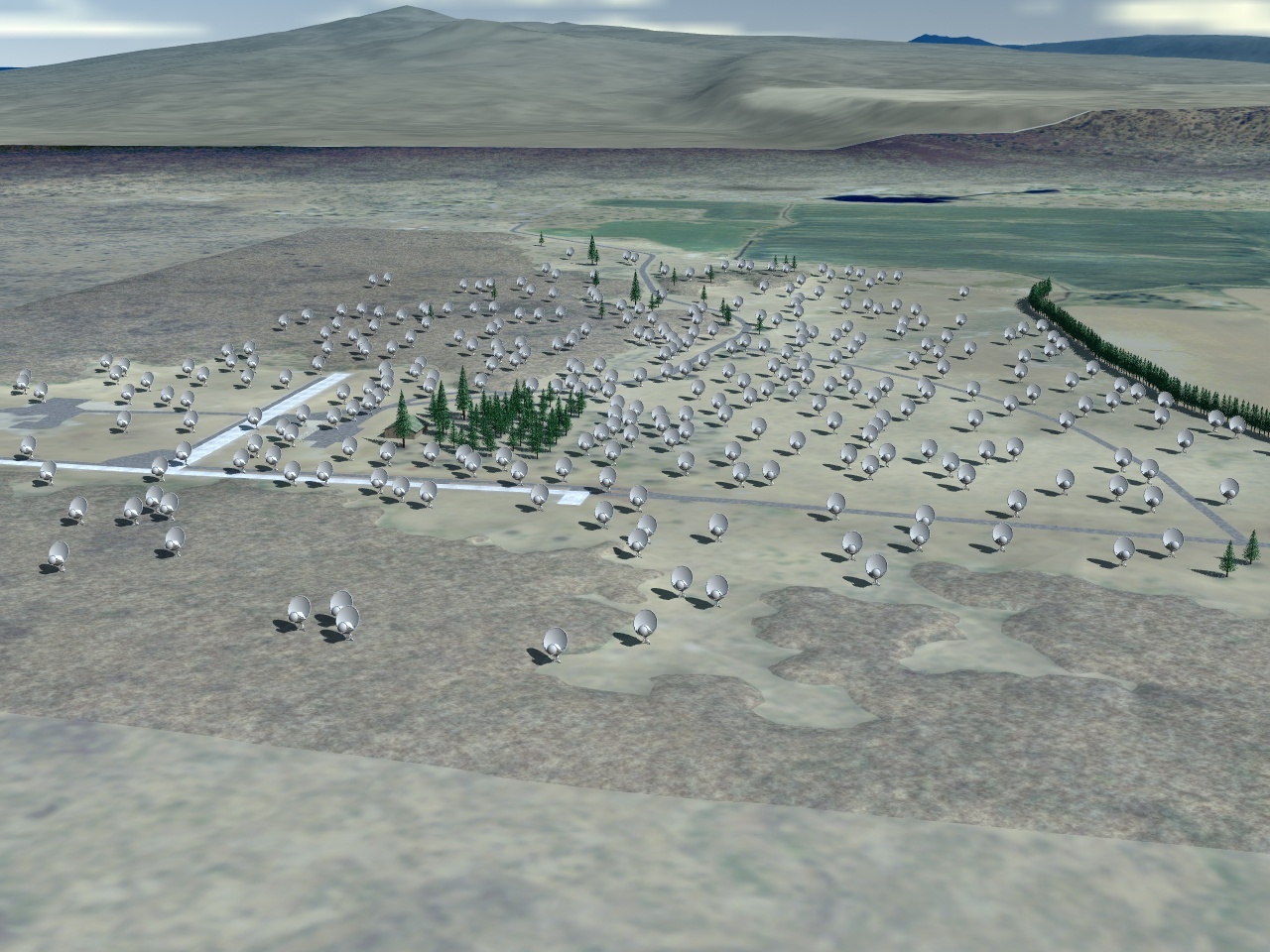
More ambitious SETI schemes are underway. The Allen Telescope Array (ATA) is a set of radio dishes that benefited from more than $30 million in gifts from Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen. Even with his support, expansion from the current set of 42 dishes to the goal of 350 is very uncertain. It may one day be possible to send a beacon and receiver hundreds of A.U. from the Earth and use the Sun as a gravitational lens to amplify and direct signals to distant targets. Future telescopes in space will allow the spectroscopic analysis of the reflected light from planets in other stellar systems. The direct detection of atmospheric chemistry that indicates life would cut through the web of anthropocentric arguments regarding technology and radio communication. In the meantime, researchers must think as broadly as possible about the nature of life. The search for life in the universe will become a truly scientific subject one step at a time.
Few scientific subjects generate as strong an emotional response as SETI. Debates between SETI optimists and pessimists can be acrimonious. Pragmatists argue that the scientific basis for optimistic calculations is flimsy and that no search strategy can be logically justified. SETI has been unpopular with some politicians, who see it as a frivolous use of taxpayers' money. NASA has had considerable trouble in funding SETI, despite the fact that it never accounted for more than 0.1% of the agency's science budget. However, popular support for SETI remains strong. "The probability of success is difficult to estimate," wrote physicists Giuseppe Cocconi and Philip Morrison in 1959 in a paper that started the modern era of SETI, "But if we never search, the chance of success is zero." Few people can resist the excitement of one of the most profound questions humans can ask: what is our place in the universe?

