Chapter 19: Life in the Universe
Chapter 1
How Science Works
- The Scientific Method
- Evidence
- Measurements
- Units and the Metric System
- Measurement Errors
- Estimation
- Dimensions
- Mass, Length, and Time
- Observations and Uncertainty
- Precision and Significant Figures
- Errors and Statistics
- Scientific Notation
- Ways of Representing Data
- Logic
- Mathematics
- Geometry
- Algebra
- Logarithms
- Testing a Hypothesis
- Case Study of Life on Mars
- Theories
- Systems of Knowledge
- The Culture of Science
- Computer Simulations
- Modern Scientific Research
- The Scope of Astronomy
- Astronomy as a Science
- A Scale Model of Space
- A Scale Model of Time
- Questions
Chapter 2
Early Astronomy
- The Night Sky
- Motions in the Sky
- Navigation
- Constellations and Seasons
- Cause of the Seasons
- The Magnitude System
- Angular Size and Linear Size
- Phases of the Moon
- Eclipses
- Auroras
- Dividing Time
- Solar and Lunar Calendars
- History of Astronomy
- Stonehenge
- Ancient Observatories
- Counting and Measurement
- Astrology
- Greek Astronomy
- Aristotle and Geocentric Cosmology
- Aristarchus and Heliocentric Cosmology
- The Dark Ages
- Arab Astronomy
- Indian Astronomy
- Chinese Astronomy
- Mayan Astronomy
- Questions
Chapter 3
The Copernican Revolution
- Ptolemy and the Geocentric Model
- The Renaissance
- Copernicus and the Heliocentric Model
- Tycho Brahe
- Johannes Kepler
- Elliptical Orbits
- Kepler's Laws
- Galileo Galilei
- The Trial of Galileo
- Isaac Newton
- Newton's Law of Gravity
- The Plurality of Worlds
- The Birth of Modern Science
- Layout of the Solar System
- Scale of the Solar System
- The Idea of Space Exploration
- Orbits
- History of Space Exploration
- Moon Landings
- International Space Station
- Manned versus Robotic Missions
- Commercial Space Flight
- Future of Space Exploration
- Living in Space
- Moon, Mars, and Beyond
- Societies in Space
- Questions
Chapter 4
Matter and Energy in the Universe
- Matter and Energy
- Rutherford and Atomic Structure
- Early Greek Physics
- Dalton and Atoms
- The Periodic Table
- Structure of the Atom
- Energy
- Heat and Temperature
- Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Velocity of Gas Particles
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Heat Transfer
- Thermal Radiation
- Wien's Law
- Radiation from Planets and Stars
- Internal Heat in Planets and Stars
- Periodic Processes
- Random Processes
- Questions
Chapter 5
The Earth-Moon System
- Earth and Moon
- Early Estimates of Earth's Age
- How the Earth Cooled
- Ages Using Radioactivity
- Radioactive Half-Life
- Ages of the Earth and Moon
- Geological Activity
- Internal Structure of the Earth and Moon
- Basic Rock Types
- Layers of the Earth and Moon
- Origin of Water on Earth
- The Evolving Earth
- Plate Tectonics
- Volcanoes
- Geological Processes
- Impact Craters
- The Geological Timescale
- Mass Extinctions
- Evolution and the Cosmic Environment
- Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans
- Weather Circulation
- Environmental Change on Earth
- The Earth-Moon System
- Geological History of the Moon
- Tidal Forces
- Effects of Tidal Forces
- Historical Studies of the Moon
- Lunar Surface
- Ice on the Moon
- Origin of the Moon
- Humans on the Moon
- Questions
Chapter 6
The Terrestrial Planets
- Studying Other Planets
- The Planets
- The Terrestrial Planets
- Mercury
- Mercury's Orbit
- Mercury's Surface
- Venus
- Volcanism on Venus
- Venus and the Greenhouse Effect
- Tectonics on Venus
- Exploring Venus
- Mars in Myth and Legend
- Early Studies of Mars
- Mars Close-Up
- Modern Views of Mars
- Missions to Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Water on Mars
- Polar Caps of Mars
- Climate Change on Mars
- Terraforming Mars
- Life on Mars
- The Moons of Mars
- Martian Meteorites
- Comparative Planetology
- Incidence of Craters
- Counting Craters
- Counting Statistics
- Internal Heat and Geological Activity
- Magnetic Fields of the Terrestrial Planets
- Mountains and Rifts
- Radar Studies of Planetary Surfaces
- Laser Ranging and Altimetry
- Gravity and Atmospheres
- Normal Atmospheric Composition
- The Significance of Oxygen
- Questions
Chapter 7
The Giant Planets and Their Moons
- The Gas Giant Planets
- Atmospheres of the Gas Giant Planets
- Clouds and Weather on Gas Giant Planets
- Internal Structure of the Gas Giant Planets
- Thermal Radiation from Gas Giant Planets
- Life on Gas Giant Planets?
- Why Giant Planets are Giant
- Gas Laws
- Ring Systems of the Giant Planets
- Structure Within Ring Systems
- The Origin of Ring Particles
- The Roche Limit
- Resonance and Harmonics
- Tidal Forces in the Solar System
- Moons of Gas Giant Planets
- Geology of Large Moons
- The Voyager Missions
- Jupiter
- Jupiter's Galilean Moons
- Jupiter's Ganymede
- Jupiter's Europa
- Jupiter's Callisto
- Jupiter's Io
- Volcanoes on Io
- Saturn
- Cassini Mission to Saturn
- Saturn's Titan
- Saturn's Enceladus
- Discovery of Uranus and Neptune
- Uranus
- Uranus' Miranda
- Neptune
- Neptune's Triton
- Pluto
- The Discovery of Pluto
- Pluto as a Dwarf Planet
- Dwarf Planets
- Questions
Chapter 8
Interplanetary Bodies
- Interplanetary Bodies
- Comets
- Early Observations of Comets
- Structure of the Comet Nucleus
- Comet Chemistry
- Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt
- Kuiper Belt
- Comet Orbits
- Life Story of Comets
- The Largest Kuiper Belt Objects
- Meteors and Meteor Showers
- Gravitational Perturbations
- Asteroids
- Surveys for Earth Crossing Asteroids
- Asteroid Shapes
- Composition of Asteroids
- Introduction to Meteorites
- Origin of Meteorites
- Types of Meteorites
- The Tunguska Event
- The Threat from Space
- Probability and Impacts
- Impact on Jupiter
- Interplanetary Opportunity
- Questions
Chapter 9
Planet Formation and Exoplanets
- Formation of the Solar System
- Early History of the Solar System
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum in a Collapsing Cloud
- Helmholtz Contraction
- Safronov and Planet Formation
- Collapse of the Solar Nebula
- Why the Solar System Collapsed
- From Planetesimals to Planets
- Accretion and Solar System Bodies
- Differentiation
- Planetary Magnetic Fields
- The Origin of Satellites
- Solar System Debris and Formation
- Gradual Evolution and a Few Catastrophies
- Chaos and Determinism
- Extrasolar Planets
- Discoveries of Exoplanets
- Doppler Detection of Exoplanets
- Transit Detection of Exoplanets
- The Kepler Mission
- Direct Detection of Exoplanets
- Properties of Exoplanets
- Implications of Exoplanet Surveys
- Future Detection of Exoplanets
- Questions
Chapter 10
Detecting Radiation from Space
- Observing the Universe
- Radiation and the Universe
- The Nature of Light
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Properties of Waves
- Waves and Particles
- How Radiation Travels
- Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
- The Doppler Effect
- Invisible Radiation
- Thermal Spectra
- The Quantum Theory
- The Uncertainty Principle
- Spectral Lines
- Emission Lines and Bands
- Absorption and Emission Spectra
- Kirchoff's Laws
- Astronomical Detection of Radiation
- The Telescope
- Optical Telescopes
- Optical Detectors
- Adaptive Optics
- Image Processing
- Digital Information
- Radio Telescopes
- Telescopes in Space
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Interferometry
- Collecting Area and Resolution
- Frontier Observatories
- Questions
Chapter 11
Our Sun: The Nearest Star
- The Sun
- The Nearest Star
- Properties of the Sun
- Kelvin and the Sun's Age
- The Sun's Composition
- Energy From Atomic Nuclei
- Mass-Energy Conversion
- Examples of Mass-Energy Conversion
- Energy From Nuclear Fission
- Energy From Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Reactions in the Sun
- The Sun's Interior
- Energy Flow in the Sun
- Collisions and Opacity
- Solar Neutrinos
- Solar Oscillations
- The Sun's Atmosphere
- Solar Chromosphere and Corona
- Sunspots
- The Solar Cycle
- The Solar Wind
- Effects of the Sun on the Earth
- Cosmic Energy Sources
- Questions
Chapter 12
Properties of Stars
- Stars
- Star Names
- Star Properties
- The Distance to Stars
- Apparent Brightness
- Absolute Brightness
- Measuring Star Distances
- Stellar Parallax
- Spectra of Stars
- Spectral Classification
- Temperature and Spectral Class
- Stellar Composition
- Stellar Motion
- Stellar Luminosity
- The Size of Stars
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law
- Stellar Mass
- Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Stellar Classification
- The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- Volume and Brightness Selected Samples
- Stars of Different Sizes
- Understanding the Main Sequence
- Stellar Structure
- Stellar Evolution
- Questions
Chapter 13
Star Birth and Death
- Star Birth and Death
- Understanding Star Birth and Death
- Cosmic Abundance of Elements
- Star Formation
- Molecular Clouds
- Young Stars
- T Tauri Stars
- Mass Limits for Stars
- Brown Dwarfs
- Young Star Clusters
- Cauldron of the Elements
- Main Sequence Stars
- Nuclear Reactions in Main Sequence Stars
- Main Sequence Lifetimes
- Evolved Stars
- Cycles of Star Life and Death
- The Creation of Heavy Elements
- Red Giants
- Horizontal Branch and Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
- Variable Stars
- Magnetic Stars
- Stellar Mass Loss
- White Dwarfs
- Supernovae
- Seeing the Death of a Star
- Supernova 1987A
- Neutron Stars and Pulsars
- Special Theory of Relativity
- General Theory of Relativity
- Black Holes
- Properties of Black Holes
- Questions
Chapter 14
The Milky Way
- The Distribution of Stars in Space
- Stellar Companions
- Binary Star Systems
- Binary and Multiple Stars
- Mass Transfer in Binaries
- Binaries and Stellar Mass
- Nova and Supernova
- Exotic Binary Systems
- Gamma Ray Bursts
- How Multiple Stars Form
- Environments of Stars
- The Interstellar Medium
- Effects of Interstellar Material on Starlight
- Structure of the Interstellar Medium
- Dust Extinction and Reddening
- Groups of Stars
- Open Star Clusters
- Globular Star Clusters
- Distances to Groups of Stars
- Ages of Groups of Stars
- Layout of the Milky Way
- William Herschel
- Isotropy and Anisotropy
- Mapping the Milky Way
- Questions
Chapter 15
Galaxies
- The Milky Way Galaxy
- Mapping the Galaxy Disk
- Spiral Structure in Galaxies
- Mass of the Milky Way
- Dark Matter in the Milky Way
- Galaxy Mass
- The Galactic Center
- Black Hole in the Galactic Center
- Stellar Populations
- Formation of the Milky Way
- Galaxies
- The Shapley-Curtis Debate
- Edwin Hubble
- Distances to Galaxies
- Classifying Galaxies
- Spiral Galaxies
- Elliptical Galaxies
- Lenticular Galaxies
- Dwarf and Irregular Galaxies
- Overview of Galaxy Structures
- The Local Group
- Light Travel Time
- Galaxy Size and Luminosity
- Mass to Light Ratios
- Dark Matter in Galaxies
- Gravity of Many Bodies
- Galaxy Evolution
- Galaxy Interactions
- Galaxy Formation
- Questions
Chapter 16
The Expanding Universe
- Galaxy Redshifts
- The Expanding Universe
- Cosmological Redshifts
- The Hubble Relation
- Relating Redshift and Distance
- Galaxy Distance Indicators
- Size and Age of the Universe
- The Hubble Constant
- Large Scale Structure
- Galaxy Clustering
- Clusters of Galaxies
- Overview of Large Scale Structure
- Dark Matter on the Largest Scales
- The Most Distant Galaxies
- Black Holes in Nearby Galaxies
- Active Galaxies
- Radio Galaxies
- The Discovery of Quasars
- Quasars
- Types of Gravitational Lensing
- Properties of Quasars
- The Quasar Power Source
- Quasars as Probes of the Universe
- Star Formation History of the Universe
- Expansion History of the Universe
- Questions
Chapter 17
Cosmology
- Cosmology
- Early Cosmologies
- Relativity and Cosmology
- The Big Bang Model
- The Cosmological Principle
- Universal Expansion
- Cosmic Nucleosynthesis
- Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- Discovery of the Microwave Background Radiation
- Measuring Space Curvature
- Cosmic Evolution
- Evolution of Structure
- Mean Cosmic Density
- Critical Density
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Age of the Universe
- Precision Cosmology
- The Future of the Contents of the Universe
- Fate of the Universe
- Alternatives to the Big Bang Model
- Space-Time
- Particles and Radiation
- The Very Early Universe
- Mass and Energy in the Early Universe
- Matter and Antimatter
- The Forces of Nature
- Fine-Tuning in Cosmology
- The Anthropic Principle in Cosmology
- String Theory and Cosmology
- The Multiverse
- The Limits of Knowledge
- Questions
Chapter 18
Life On Earth
- Nature of Life
- Chemistry of Life
- Molecules of Life
- The Origin of Life on Earth
- Origin of Complex Molecules
- Miller-Urey Experiment
- Pre-RNA World
- RNA World
- From Molecules to Cells
- Metabolism
- Anaerobes
- Extremophiles
- Thermophiles
- Psychrophiles
- Xerophiles
- Halophiles
- Barophiles
- Acidophiles
- Alkaliphiles
- Radiation Resistant Biology
- Importance of Water for Life
- Hydrothermal Systems
- Silicon Versus Carbon
- DNA and Heredity
- Life as Digital Information
- Synthetic Biology
- Life in a Computer
- Natural Selection
- Tree Of Life
- Evolution and Intelligence
- Culture and Technology
- The Gaia Hypothesis
- Life and the Cosmic Environment
Lowell and Canals on Mars

Percival Lowell drove his construction team hard. It was 1894, and up on a high plateau in the northern part of the Arizona Territory near Flagstaff, the wealthy Bostonian was racing to complete an observatory with a 24-inch telescope. He was anxious for the completion of the observatory because the large telescope would finally allow the surface features of Mars, which would be making its closest approach to Earth in 15 years, to be distinguished. It would only be a few months that Mars would be this accessible, looming large in the night sky. After a time that seemed like an eternity, the building was finally complete. Lowell excitedly turned his telescope toward the red planet. He noted Mars' polar caps and the irregular complexion of the surface. But above all, his attention was captured by what appeared to be a set of linear markings, what he perceived as a hundred "canals" covering the planet.
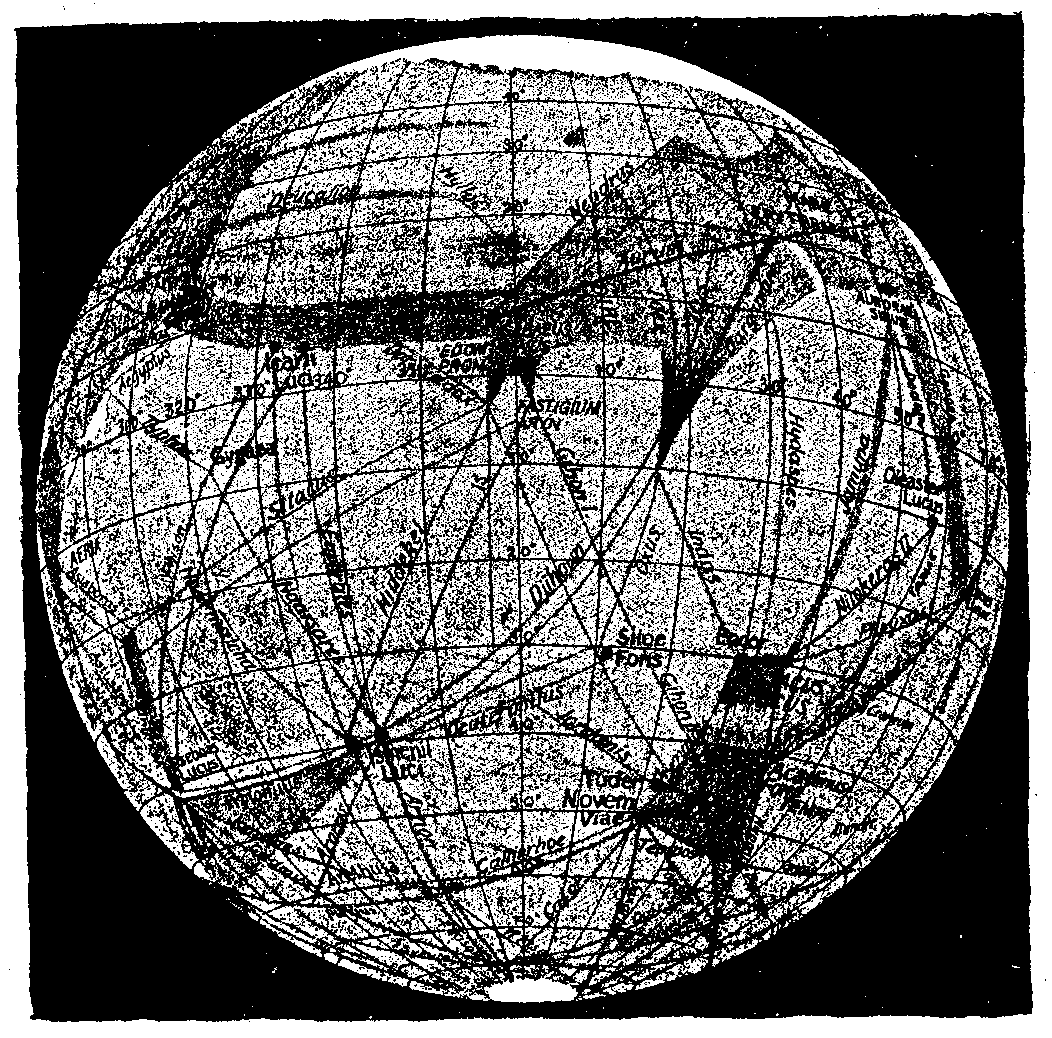
Lowell was not the first person to see canals on Mars and he certainly was not the last. During the two previous close approaches of Mars to Earth, a couple of Italian astronomers also observed unique features on the surface. They made note of scraggly markings that they called "canali," or channels. When American journalists caught wind of the story, they mistranslated the word as "canals". Although similar to the true translation, the word canals carried with it the inference of intelligent engineering. Upon hearing about what the Italians had seen, Lowell wanted to look for similar features, only with a more powerful telescope. Lowell subsequently repeated the observations of the Italian astronomers and news of his discovery spread quickly. Even the sober Wall Street Journal picked up the Mars fever, writing in a year-end summary of major events that, "the most extraordinary event of the year is the proof afforded by astronomical observations that conscious, intelligent life exists on Mars."
Were Lowell's observations sufficient to serve as evidence of life on Mars? Lowell himself was thoroughly convinced. He reasoned that the linear features on Mars represented formations that could not possibly have occurred naturally. Lowell concluded that an intelligent civilization inhabited Mars. He proposed that, due to a lack of water on Mars, this civilization was struggling to stay alive. Therefore, Lowell said, the Martians had constructed water canals to transport water from the frozen polar caps to the arid lower latitudes. He admitted that his new telescope did not actually have the resolution to truly see the canals themselves. The dark lines that he saw were justified as strips of lush vegetation that were cultivated by water irrigation from the canals, thereby making the canals more visible from Earth.
Born in 1855 into an aristocratic Boston family, Percival Lowell made his money in trade. After graduating from Harvard, he traveled the world and became a scholar of Asian history and culture. But his true love was astronomy. Excited about the observations made with his new telescope, Lowell wrote a book entitled Mars in 1895. In this popular book, Lowell strongly and persuasively presented his case for life on Mars. He wrote: "That beings constituted physically as we are would find Mars a most uncomfortable place is pretty certain. But there is nothing in the world or beyond it to prevent, so far as we know, a fish with gills, for example, from being a most superior person. A fish doubtless imagines life outside water to be impossible; and similarly to argue that life of an order as high as our own, or higher, is impossible because of less air to breathe is to argue, not as a philosopher but as a fish."

Despite the publicity and popularity of Lowell's observations, many respected astronomers disagreed with his findings. During those times, astronomical photography was rudimentary and inefficient, so the only images of Mars were laboriously drawn by hand. There were a few professional astronomers that also claimed to see the canals, but there were many more that did not. It has been rumored that colleagues of Lowell challenged his hand-drawn maps of Mars. Fellow astronomers at the observatory drew lines on a ball the size of a basketball. They then placed a small telescope at a precise distance that would replicate the resolution achieved by the 24-inch telescope focused on the real planet Mars. Lowell's colleagues then challenged him to draw a map of the "canals" drawn on the ball. Upon comparison of the ball and the map, the astronomers found absolutely no correlation between the lines that Lowell drew and the lines that were drawn on the map. Had Lowell allowed his desire to see canals on Mars to influence his observations? This instance, coupled with astronomers' own observations, caused many to speak out against Lowell. For example, the director of Lick Observatory described Lowell's writings as "misleading and unfortunate half-truths." The head of the Mars observing section of the British Astronomical Society wrote: "Had it not been for the foreknowledge that the canals are there, I would have missed at least three-quarters of them."

The next close approach of Mars to Earth was in 1910. By this time astronomers had access to better methods for capturing images of planets and larger telescopes that yielded better resolution. Images of Mars now displayed the "canals" as highly irregular and disconnected surface features. Moreover, astronomers had made further observations that suggested Mars to be too dry to support large life forms. Instead of water, the polar caps are made of carbon dioxide, more commonly known as dry ice. Alfred Wallace, the co-creator of the theory of natural selection with Charles Darwin, wrote ardently: "Not only is Mars not inhabited by intelligent beings as Mr. Lowell postulates, it is absolutely uninhabitable." Lowell had fallen victim to the power of suggestion and the dangers of allowing subjectivity to influence his scientific conclusions.

Despite the new evidence to the contrary, public belief in canals and life on Mars did not subside. Images of Mars with intricate canal systems were depicted in school science textbooks well into the 1950s. Lowell's mistake about Mars started a century of speculation about life on Mars that is especially pervasive in popular culture. The first example of this was written within three years of Lowell's book. H.G. Wells published The War of the Worlds, a memorable and influential piece of science fiction. In this work, H.G. Wells described intelligent creatures living on Mars. The civilization on Mars realizes that the canals are not enough to sustain life on the dying planet. In desperation, the Martians seek a new source of water by invading Earth with superior military technology. The result is their sickness and demise due to common terrestrial microorganisms. Stemming from Lowell's observations over a century ago and sparked by The War of the Worlds, many books, movies, songs, and other media sources have been heavily influenced by our curiosity about life in the universe.

