Chapter 18: Life On Earth
Chapter 1
How Science Works
- The Scientific Method
- Evidence
- Measurements
- Units and the Metric System
- Measurement Errors
- Estimation
- Dimensions
- Mass, Length, and Time
- Observations and Uncertainty
- Precision and Significant Figures
- Errors and Statistics
- Scientific Notation
- Ways of Representing Data
- Logic
- Mathematics
- Geometry
- Algebra
- Logarithms
- Testing a Hypothesis
- Case Study of Life on Mars
- Theories
- Systems of Knowledge
- The Culture of Science
- Computer Simulations
- Modern Scientific Research
- The Scope of Astronomy
- Astronomy as a Science
- A Scale Model of Space
- A Scale Model of Time
- Questions
Chapter 2
Early Astronomy
- The Night Sky
- Motions in the Sky
- Navigation
- Constellations and Seasons
- Cause of the Seasons
- The Magnitude System
- Angular Size and Linear Size
- Phases of the Moon
- Eclipses
- Auroras
- Dividing Time
- Solar and Lunar Calendars
- History of Astronomy
- Stonehenge
- Ancient Observatories
- Counting and Measurement
- Astrology
- Greek Astronomy
- Aristotle and Geocentric Cosmology
- Aristarchus and Heliocentric Cosmology
- The Dark Ages
- Arab Astronomy
- Indian Astronomy
- Chinese Astronomy
- Mayan Astronomy
- Questions
Chapter 3
The Copernican Revolution
- Ptolemy and the Geocentric Model
- The Renaissance
- Copernicus and the Heliocentric Model
- Tycho Brahe
- Johannes Kepler
- Elliptical Orbits
- Kepler's Laws
- Galileo Galilei
- The Trial of Galileo
- Isaac Newton
- Newton's Law of Gravity
- The Plurality of Worlds
- The Birth of Modern Science
- Layout of the Solar System
- Scale of the Solar System
- The Idea of Space Exploration
- Orbits
- History of Space Exploration
- Moon Landings
- International Space Station
- Manned versus Robotic Missions
- Commercial Space Flight
- Future of Space Exploration
- Living in Space
- Moon, Mars, and Beyond
- Societies in Space
- Questions
Chapter 4
Matter and Energy in the Universe
- Matter and Energy
- Rutherford and Atomic Structure
- Early Greek Physics
- Dalton and Atoms
- The Periodic Table
- Structure of the Atom
- Energy
- Heat and Temperature
- Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Velocity of Gas Particles
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Heat Transfer
- Thermal Radiation
- Wien's Law
- Radiation from Planets and Stars
- Internal Heat in Planets and Stars
- Periodic Processes
- Random Processes
- Questions
Chapter 5
The Earth-Moon System
- Earth and Moon
- Early Estimates of Earth's Age
- How the Earth Cooled
- Ages Using Radioactivity
- Radioactive Half-Life
- Ages of the Earth and Moon
- Geological Activity
- Internal Structure of the Earth and Moon
- Basic Rock Types
- Layers of the Earth and Moon
- Origin of Water on Earth
- The Evolving Earth
- Plate Tectonics
- Volcanoes
- Geological Processes
- Impact Craters
- The Geological Timescale
- Mass Extinctions
- Evolution and the Cosmic Environment
- Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans
- Weather Circulation
- Environmental Change on Earth
- The Earth-Moon System
- Geological History of the Moon
- Tidal Forces
- Effects of Tidal Forces
- Historical Studies of the Moon
- Lunar Surface
- Ice on the Moon
- Origin of the Moon
- Humans on the Moon
- Questions
Chapter 6
The Terrestrial Planets
- Studying Other Planets
- The Planets
- The Terrestrial Planets
- Mercury
- Mercury's Orbit
- Mercury's Surface
- Venus
- Volcanism on Venus
- Venus and the Greenhouse Effect
- Tectonics on Venus
- Exploring Venus
- Mars in Myth and Legend
- Early Studies of Mars
- Mars Close-Up
- Modern Views of Mars
- Missions to Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Water on Mars
- Polar Caps of Mars
- Climate Change on Mars
- Terraforming Mars
- Life on Mars
- The Moons of Mars
- Martian Meteorites
- Comparative Planetology
- Incidence of Craters
- Counting Craters
- Counting Statistics
- Internal Heat and Geological Activity
- Magnetic Fields of the Terrestrial Planets
- Mountains and Rifts
- Radar Studies of Planetary Surfaces
- Laser Ranging and Altimetry
- Gravity and Atmospheres
- Normal Atmospheric Composition
- The Significance of Oxygen
- Questions
Chapter 7
The Giant Planets and Their Moons
- The Gas Giant Planets
- Atmospheres of the Gas Giant Planets
- Clouds and Weather on Gas Giant Planets
- Internal Structure of the Gas Giant Planets
- Thermal Radiation from Gas Giant Planets
- Life on Gas Giant Planets?
- Why Giant Planets are Giant
- Gas Laws
- Ring Systems of the Giant Planets
- Structure Within Ring Systems
- The Origin of Ring Particles
- The Roche Limit
- Resonance and Harmonics
- Tidal Forces in the Solar System
- Moons of Gas Giant Planets
- Geology of Large Moons
- The Voyager Missions
- Jupiter
- Jupiter's Galilean Moons
- Jupiter's Ganymede
- Jupiter's Europa
- Jupiter's Callisto
- Jupiter's Io
- Volcanoes on Io
- Saturn
- Cassini Mission to Saturn
- Saturn's Titan
- Saturn's Enceladus
- Discovery of Uranus and Neptune
- Uranus
- Uranus' Miranda
- Neptune
- Neptune's Triton
- Pluto
- The Discovery of Pluto
- Pluto as a Dwarf Planet
- Dwarf Planets
- Questions
Chapter 8
Interplanetary Bodies
- Interplanetary Bodies
- Comets
- Early Observations of Comets
- Structure of the Comet Nucleus
- Comet Chemistry
- Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt
- Kuiper Belt
- Comet Orbits
- Life Story of Comets
- The Largest Kuiper Belt Objects
- Meteors and Meteor Showers
- Gravitational Perturbations
- Asteroids
- Surveys for Earth Crossing Asteroids
- Asteroid Shapes
- Composition of Asteroids
- Introduction to Meteorites
- Origin of Meteorites
- Types of Meteorites
- The Tunguska Event
- The Threat from Space
- Probability and Impacts
- Impact on Jupiter
- Interplanetary Opportunity
- Questions
Chapter 9
Planet Formation and Exoplanets
- Formation of the Solar System
- Early History of the Solar System
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum in a Collapsing Cloud
- Helmholtz Contraction
- Safronov and Planet Formation
- Collapse of the Solar Nebula
- Why the Solar System Collapsed
- From Planetesimals to Planets
- Accretion and Solar System Bodies
- Differentiation
- Planetary Magnetic Fields
- The Origin of Satellites
- Solar System Debris and Formation
- Gradual Evolution and a Few Catastrophies
- Chaos and Determinism
- Extrasolar Planets
- Discoveries of Exoplanets
- Doppler Detection of Exoplanets
- Transit Detection of Exoplanets
- The Kepler Mission
- Direct Detection of Exoplanets
- Properties of Exoplanets
- Implications of Exoplanet Surveys
- Future Detection of Exoplanets
- Questions
Chapter 10
Detecting Radiation from Space
- Observing the Universe
- Radiation and the Universe
- The Nature of Light
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Properties of Waves
- Waves and Particles
- How Radiation Travels
- Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
- The Doppler Effect
- Invisible Radiation
- Thermal Spectra
- The Quantum Theory
- The Uncertainty Principle
- Spectral Lines
- Emission Lines and Bands
- Absorption and Emission Spectra
- Kirchoff's Laws
- Astronomical Detection of Radiation
- The Telescope
- Optical Telescopes
- Optical Detectors
- Adaptive Optics
- Image Processing
- Digital Information
- Radio Telescopes
- Telescopes in Space
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Interferometry
- Collecting Area and Resolution
- Frontier Observatories
- Questions
Chapter 11
Our Sun: The Nearest Star
- The Sun
- The Nearest Star
- Properties of the Sun
- Kelvin and the Sun's Age
- The Sun's Composition
- Energy From Atomic Nuclei
- Mass-Energy Conversion
- Examples of Mass-Energy Conversion
- Energy From Nuclear Fission
- Energy From Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Reactions in the Sun
- The Sun's Interior
- Energy Flow in the Sun
- Collisions and Opacity
- Solar Neutrinos
- Solar Oscillations
- The Sun's Atmosphere
- Solar Chromosphere and Corona
- Sunspots
- The Solar Cycle
- The Solar Wind
- Effects of the Sun on the Earth
- Cosmic Energy Sources
- Questions
Chapter 12
Properties of Stars
- Stars
- Star Names
- Star Properties
- The Distance to Stars
- Apparent Brightness
- Absolute Brightness
- Measuring Star Distances
- Stellar Parallax
- Spectra of Stars
- Spectral Classification
- Temperature and Spectral Class
- Stellar Composition
- Stellar Motion
- Stellar Luminosity
- The Size of Stars
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law
- Stellar Mass
- Hydrostatic Equilibrium
- Stellar Classification
- The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- Volume and Brightness Selected Samples
- Stars of Different Sizes
- Understanding the Main Sequence
- Stellar Structure
- Stellar Evolution
- Questions
Chapter 13
Star Birth and Death
- Star Birth and Death
- Understanding Star Birth and Death
- Cosmic Abundance of Elements
- Star Formation
- Molecular Clouds
- Young Stars
- T Tauri Stars
- Mass Limits for Stars
- Brown Dwarfs
- Young Star Clusters
- Cauldron of the Elements
- Main Sequence Stars
- Nuclear Reactions in Main Sequence Stars
- Main Sequence Lifetimes
- Evolved Stars
- Cycles of Star Life and Death
- The Creation of Heavy Elements
- Red Giants
- Horizontal Branch and Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
- Variable Stars
- Magnetic Stars
- Stellar Mass Loss
- White Dwarfs
- Supernovae
- Seeing the Death of a Star
- Supernova 1987A
- Neutron Stars and Pulsars
- Special Theory of Relativity
- General Theory of Relativity
- Black Holes
- Properties of Black Holes
- Questions
Chapter 14
The Milky Way
- The Distribution of Stars in Space
- Stellar Companions
- Binary Star Systems
- Binary and Multiple Stars
- Mass Transfer in Binaries
- Binaries and Stellar Mass
- Nova and Supernova
- Exotic Binary Systems
- Gamma Ray Bursts
- How Multiple Stars Form
- Environments of Stars
- The Interstellar Medium
- Effects of Interstellar Material on Starlight
- Structure of the Interstellar Medium
- Dust Extinction and Reddening
- Groups of Stars
- Open Star Clusters
- Globular Star Clusters
- Distances to Groups of Stars
- Ages of Groups of Stars
- Layout of the Milky Way
- William Herschel
- Isotropy and Anisotropy
- Mapping the Milky Way
- Questions
Chapter 15
Galaxies
- The Milky Way Galaxy
- Mapping the Galaxy Disk
- Spiral Structure in Galaxies
- Mass of the Milky Way
- Dark Matter in the Milky Way
- Galaxy Mass
- The Galactic Center
- Black Hole in the Galactic Center
- Stellar Populations
- Formation of the Milky Way
- Galaxies
- The Shapley-Curtis Debate
- Edwin Hubble
- Distances to Galaxies
- Classifying Galaxies
- Spiral Galaxies
- Elliptical Galaxies
- Lenticular Galaxies
- Dwarf and Irregular Galaxies
- Overview of Galaxy Structures
- The Local Group
- Light Travel Time
- Galaxy Size and Luminosity
- Mass to Light Ratios
- Dark Matter in Galaxies
- Gravity of Many Bodies
- Galaxy Evolution
- Galaxy Interactions
- Galaxy Formation
- Questions
Chapter 16
The Expanding Universe
- Galaxy Redshifts
- The Expanding Universe
- Cosmological Redshifts
- The Hubble Relation
- Relating Redshift and Distance
- Galaxy Distance Indicators
- Size and Age of the Universe
- The Hubble Constant
- Large Scale Structure
- Galaxy Clustering
- Clusters of Galaxies
- Overview of Large Scale Structure
- Dark Matter on the Largest Scales
- The Most Distant Galaxies
- Black Holes in Nearby Galaxies
- Active Galaxies
- Radio Galaxies
- The Discovery of Quasars
- Quasars
- Types of Gravitational Lensing
- Properties of Quasars
- The Quasar Power Source
- Quasars as Probes of the Universe
- Star Formation History of the Universe
- Expansion History of the Universe
- Questions
Chapter 17
Cosmology
- Cosmology
- Early Cosmologies
- Relativity and Cosmology
- The Big Bang Model
- The Cosmological Principle
- Universal Expansion
- Cosmic Nucleosynthesis
- Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- Discovery of the Microwave Background Radiation
- Measuring Space Curvature
- Cosmic Evolution
- Evolution of Structure
- Mean Cosmic Density
- Critical Density
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Age of the Universe
- Precision Cosmology
- The Future of the Contents of the Universe
- Fate of the Universe
- Alternatives to the Big Bang Model
- Space-Time
- Particles and Radiation
- The Very Early Universe
- Mass and Energy in the Early Universe
- Matter and Antimatter
- The Forces of Nature
- Fine-Tuning in Cosmology
- The Anthropic Principle in Cosmology
- String Theory and Cosmology
- The Multiverse
- The Limits of Knowledge
- Questions
Chapter 19
Life in the Universe
- Life in the Universe
- Astrobiology
- Life Beyond Earth
- Sites for Life
- Complex Molecules in Space
- Life in the Solar System
- Lowell and Canals on Mars
- Implications of Life on Mars
- Extreme Environments in the Solar System
- Rare Earth Hypothesis
- Are We Alone?
- Unidentified Flying Objects or UFOs
- The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
- The Drake Equation
- The History of SETI
- Recent SETI Projects
- Recognizing a Message
- The Best Way to Communicate
- The Fermi Question
- The Anthropic Principle
- Where Are They?
From Molecules to Cells

How did the first life forms on our planet evolve from a mere chemical broth? It is a matter of conjecture at what point a complex assemblage of molecules deserves to be called a life form. We do not know how and when those first primitive life forms emerged, but scientists have come up with a likely scenario. It is generally agreed that the appearance of life depended on the changing conditions on early Earth. The Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago, with a primitive atmosphere containing gases rich in carbon and nitrogen and deficient in hydrogen and oxygen. During its first 100 million years, the Earth was bombarded by many rocky fragments, some of which may have been as large as the Moon. Such impacts would have vaporized the oceans and a large amount of the Earth's crust. Material rich in hydrogen, oxygen, and complex molecules arrived somewhat later, in the form of comets and objects from the outer solar system. The early Earth was a strange and almost unrecognizable place, yet life first formed in this environment.
The next step after the first replicating molecules — aggregating complex organic molecules into cell-like structures — must have taken place in the 500 million years after the Earth formed. Although some of the processes can occur in dry environments, liquid water was probably critical to biochemical evolution because it provided a medium in which materials could move and stick together. One botanist has commented that "all cells, of all living organisms, are strictly aquatic creatures." Any land-based organism is merely a protective shell filled up with millions of aquatic cells.
Biological processes cannot develop unless they are set apart from the environment and protected from dilution. Some sort of compartment or membrane is required to form a cell. Florida biologist Sidney Fox has shown that simple heating of dry amino acids (as might happen on a dry planet) can create protein molecules. Once water is added, these proteins assume the shape of round, cell-like objects called proteinoids, which take in material from the surrounding liquid, grow by attaching to each other, and divide. Though they are not considered living, they resemble bacteria so much that experts have trouble distinguishing them by appearance. Possibly related to proteinoids are objects discovered in the 1930s by Dutch chemist H.G. Bungenberg de Jong. When proteins are mixed in water solutions with other complex molecules, both sets of substances spontaneously accumulate into cell-sized clusters called coacervates. The remaining fluid is almost entirely free of complex organic molecules.

The next step towards recognizable life is even more uncertain. If organic molecules or coacervates are present in a pool of water, they will be left in the pool as the water evaporates. In this way, evaporation of the water in tidewater pools provided high, localized concentrations of amino acids, proteins, and other molecules, allowing cell-like structures to form. The cell-like structures in the primeval pools of "organic broth" could have begun reacting with fluids in the pools and with each other, accumulating more molecules and growing more complex. This concept was first suggested by Charles Darwin, who speculated on "some warm little pond" where life might have begun. Eventually, these early cells could have evolved into biochemical systems capable of reproducing and increasing in complexity. A cell is a sophisticated chemical factory. It is not surprising that we cannot duplicate this evolution in the laboratory, since it took half a billion years on Earth.
The earliest biological systems capable of independent life were bacteria. Bacterial cells are prokaryotes, cells without nuclei that contain a single long strand of DNA with several thousand genes. Indirect evidence of bacteria has been found in the Earth's oldest rocks. The evidence consists of carbon isotopes of possible biological origin found in a 3.8-billion-year-old rock from western Greenland. The earliest "probable" evidence for life is a colony of stromatolites — cabbage-like mats of sediment rimmed with bacteria and blue-green algae. These primitive life forms date from 3.5 to 3.6 billion years ago and have been found in Africa and Australia. Fossils of methane-producing bacteria have also been found in 3.4-billion-year-old rocks in South Africa.
The fact that the oldest fossils are younger than the oldest rocks may not be significant. Life may have originated considerably earlier. However, life probably could not have evolved much before 4.1 billion years ago because of the intense early meteoric bombardment and the possible ocean of liquid lava covering much of the Earth's crust. As paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould has observed, life arose "as soon as it could; perhaps it was as inevitable as quartz or feldspar." One set of calculations has been used to argue that life might have originated several times on the early Earth and that all life today would have descended from just one of the origination events. It is also noteworthy that the early Australian stromatolites prospered in strange and hostile environments. Evidence suggests that these organisms lived near shallow hydro-thermal vents dominated by island volcanism. In an atmosphere with almost no oxygen, they metabolized the gas hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which is toxic to most modern life forms.
Using fossil and chemical evidence, and a little speculation, we can tell the story of life on Earth. For around 2 billion years, prokaryotes ruled the oceans of the Earth. Life remained in the oceans, where liquid water provided a supporting and protective environment. Organisms were mostly soft-bodied and rarely produced fossils, so their development is hard to trace. The land was barren. Some areas must have looked like today's deserts or like Mars. Some areas were moist and washed by rains, but instead of luxurious forests, there were only bare acres, eroded gullies, and grand canyons. Brown vistas stretched to the sea.
Gradually, life went through a remarkable transition. Early prokaryotes survived and evolved by using the organic compounds that were present in warm ponds and by using hydrogen sulfide as an energy source. However, as this source of food was extinguished by changes in the Earth's atmosphere, some prokaryotes invented photosynthesis. Photosynthesis allows the conversion of sunlight into stored chemical energy for future use. This fundamental process allowed the proliferation of advanced forms of life and allowed life to endure for a cosmic time scale. Life's destiny became coupled to the fusion energy source deep in the Sun's interior.
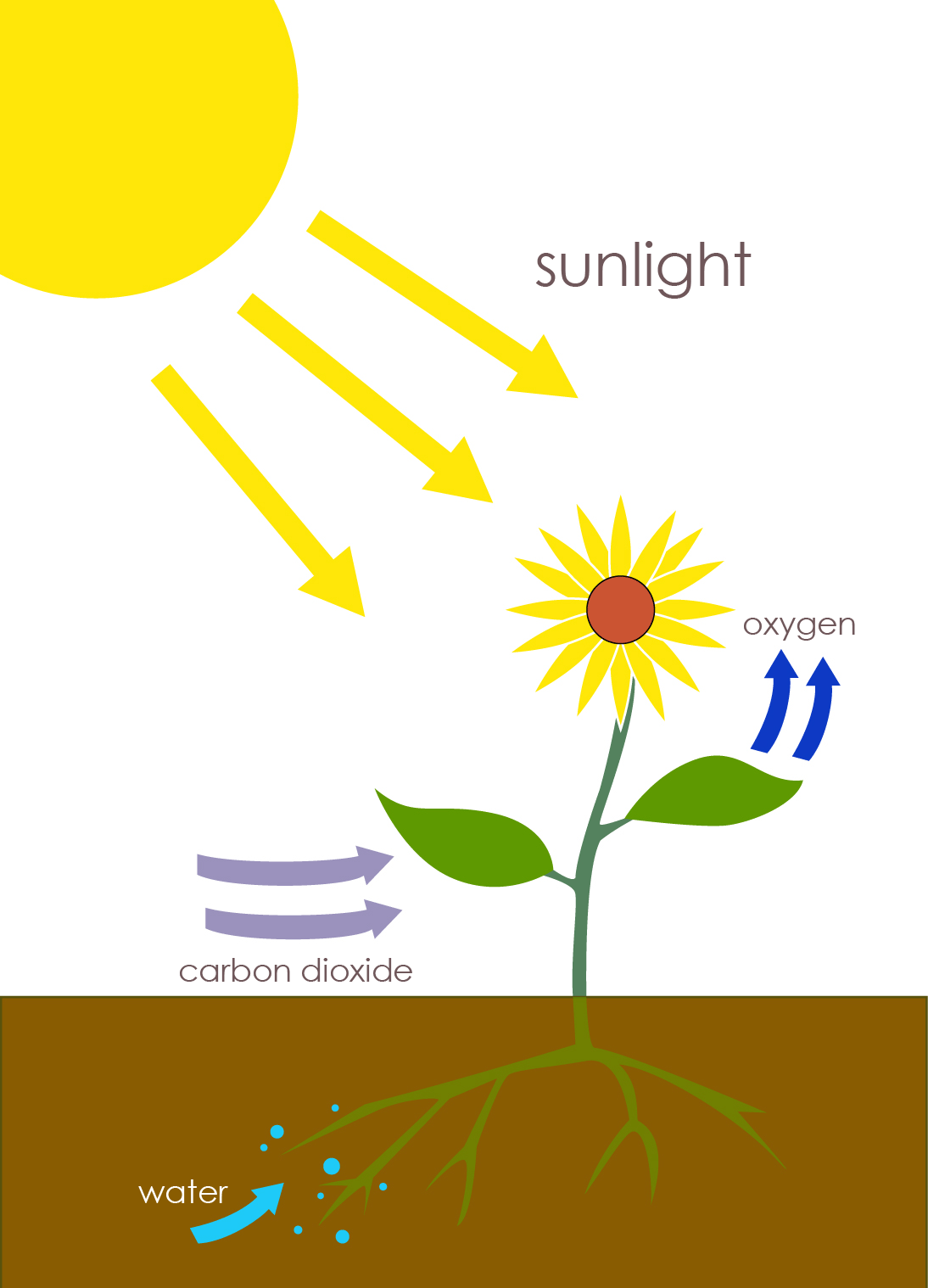
One result of the invention of photosynthesis was the release of oxygen into the Earth's atmosphere. Essentially all of the free oxygen on which modern life forms depend (including us!) was dumped into the atmosphere by microscopic organisms billions of years ago. At first, this gas was nothing more than a waste product — oxygen was actually poisonous to the first organisms! Over time, organisms evolved that could use oxygen in their metabolism, and the oxygen content began to rise to the modern value of 21%. The atmosphere therefore evolved from more reducing conditions (dominated by hydrogen compounds) to oxidizing conditions (dominated by oxygen compounds). As evidence of this change, we find that oxidized sediments are rare before 2 billion years ago and common afterward. Oxygen production modified the whole environment. Solar UV radiation broke down some O2 molecules and the free oxygen atoms joined with other O2 molecules to make ozone (O3) molecules. The result was the formation of an ozone layer high in the Earth's atmosphere, which absorbs solar UV radiation and thus protects organisms on the surface.
About 1.4 billion years ago, life stepped upward in complexity. Cells called eukaryotes developed; a membrane at the center of these cells holds the DNA. Eukaryotes contain hundreds of times more genetic material than prokaryotes, with a corresponding increase in the complexity of cell function. New types of organisms appear in the fossil record: they are capable of oxygen metabolism, and, although less resistant to UV damage, they are able to flourish because of the new ozone layer. Earth then witnesses the expansion of life from the sea onto the land, a step as momentous as the contemplated colonization of other planets by us! As organisms continued to reproduce, some of them invented sex. Sexual reproduction allows an offspring to receive half of its genes from each parent. All eukaryotic cells can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction causes the gene combinations to change from generation to generation. Such new combinations in turn facilitate the experimentation and adaptation that allows organisms to survive in a hostile and changing environment.

